 ">
">
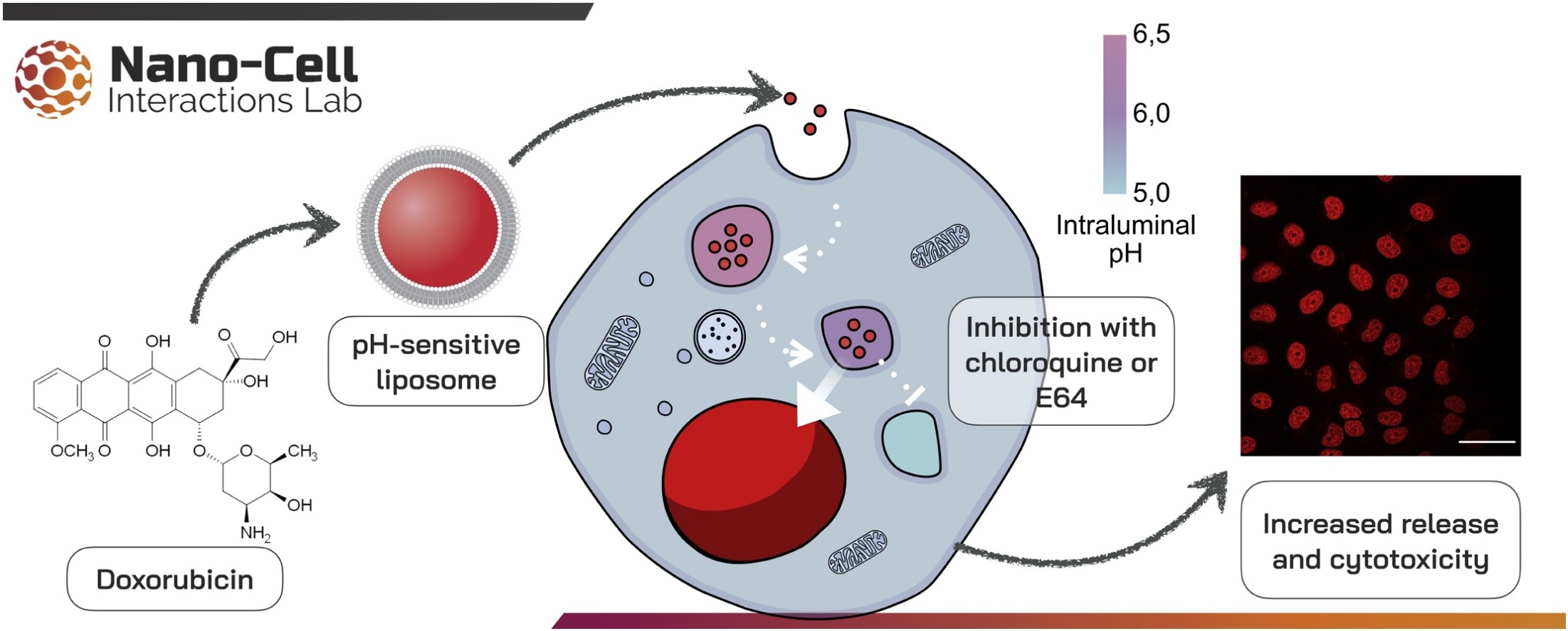
This paper shows that the release of drugs from pH-related liposomes is more complicated than just dependent on decreases in intracellular vesicles' pH. Chloroquine, an acidification inhibitor, increased doxorubicin's release and cytotoxicity of pH-related liposomes. A similar effect was observed for E64d, a cysteine protease inhibitor. Doxorubicin is chemotherapy widely used in the clinic; our work provided knowledge for developing rational strategies to improve smart drugs capable of preventing the advancement of tumors.
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2021
 ">
">
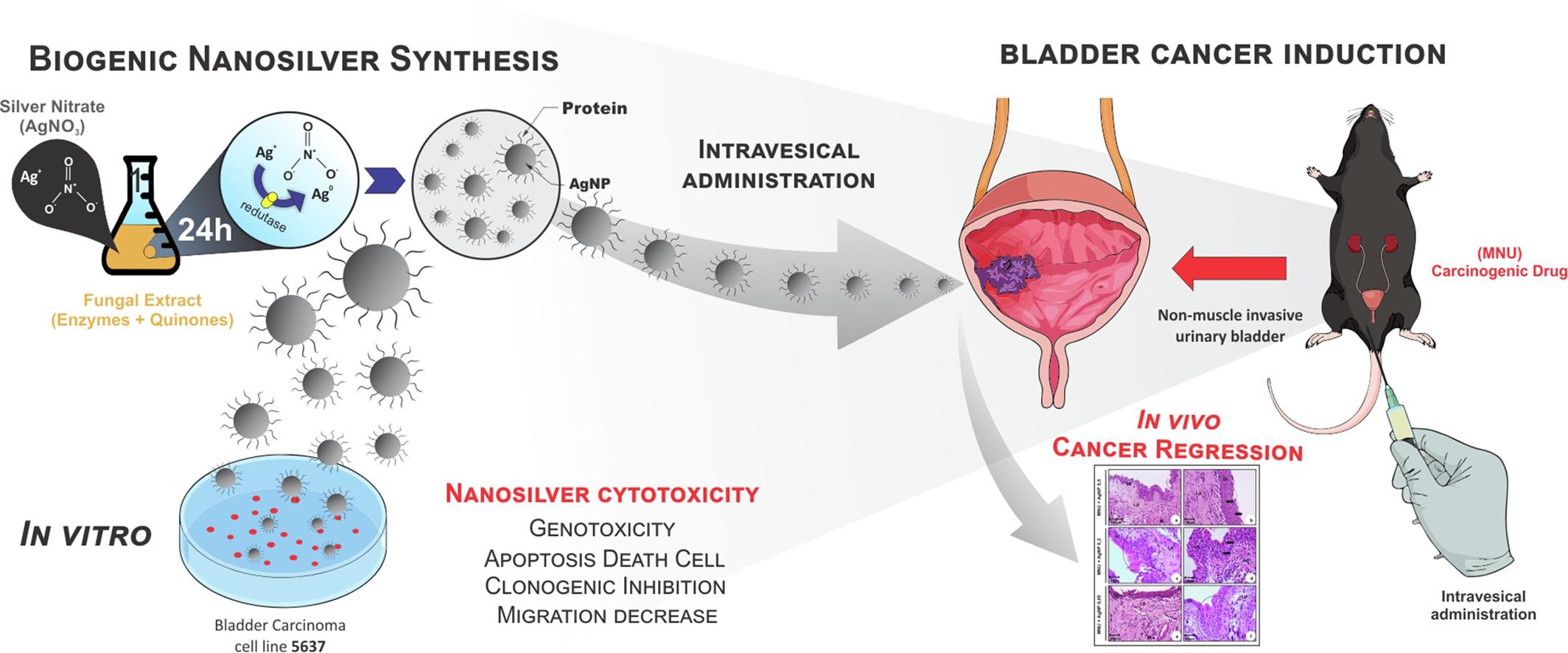
Bladder cancer is still a cancer of high prevalence and challenging to treat. This work demonstrates the anti-tumor mechanisms of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) in vitro and in vivo. Overall, these findings showed that AgNP could be an economical alternative and a promising candidate for bladder cancer treatment.
European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2020
 ">
">
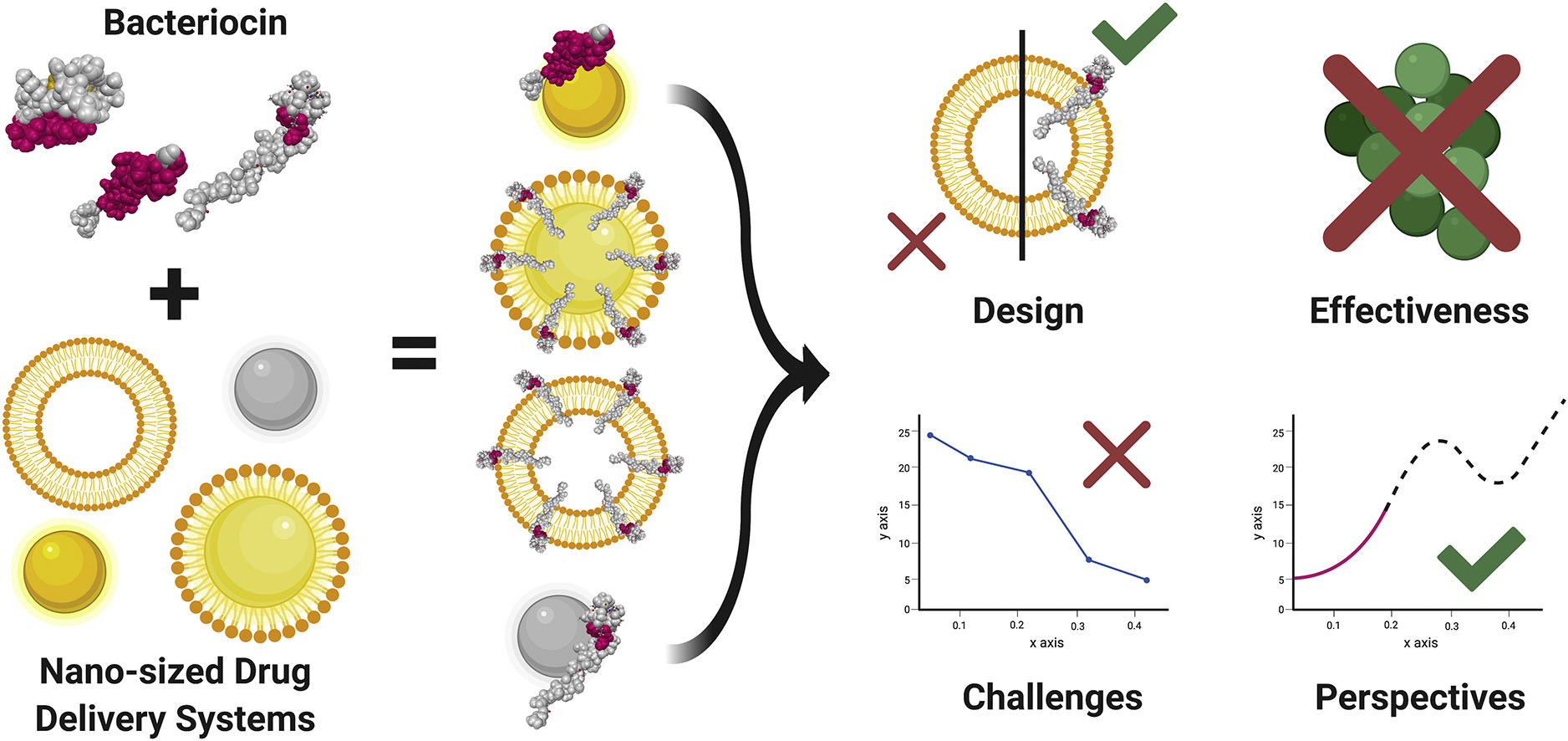
In this review, we discussed the challenges that bacteriocins, peptide antimicrobials, need to overcome before reaching the market. Also, we address strategies to enhance future generations of nanometer-sized bacteriocin drug delivery systems.
Journal of Controlled Release, 2020
We developed the PyScratch, a simple tool for processing spatial and temporal information in an automated fashion from wound healing and scratch assays. PyScratch offers a user-friendly interface allowing researches with little or no programming skills to perform quantitative analysis of in vitro scratch assays.
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2020
 ">
">
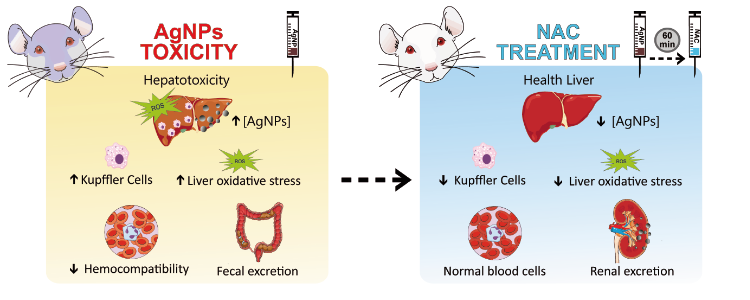
The increasing use of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in consumer products raises the risk of human toxicity. Currently, there are no therapeutic options or established treatment protocols in cases of AgNPs intoxication. Here, we investigated the use of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) against the systemic toxic effects of AgNPs (79.3 nm) in rats. Treatment with a single intraperitoneal injection of NAC (1 g/kg b.w.) one hour after AgNPs exposure significantly attenuated all toxic effects evaluated and altered the bioaccumulation and release patterns of AgNPs in rats. The findings show that NAC may be a promising candidate for clinical management of AgNPs intoxication.
Nanotoxicology, 2019
 ">
">
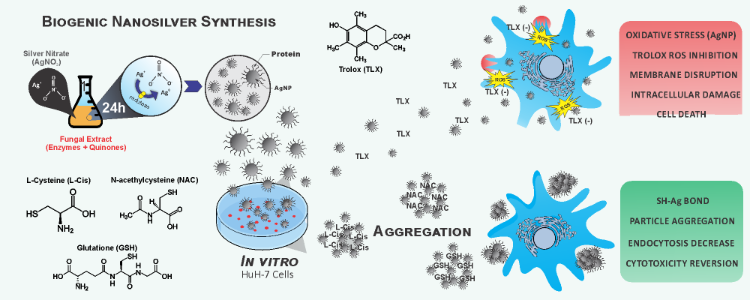
Here, we studied the molecular interaction between the thiol-antioxidants (N-acetyl-L-Cysteine, L-Cysteine, and glutathione) or non-thiol-antioxidants (Trolox) with chemically and biologically synthesized AgNP. Both antioxidants could mitigate ROS production in Huh-7 hepatocarcinoma cells, but only thiol-antioxidants could prevent the cytotoxic effect, directly binding to the AgNP leading to aggregation. Our findings show that data interpretation might not be straightforward when using thiol-antioxidants to study the interactions between metallic nanoparticles and cells. This artifact exemplifies potential pitfalls that could hinder the progress of nanotechnology and the understanding of the nanotoxicity mechanism.
Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, Feb 2020
 ">
">
This chapter provided a review of the state-of-the-art carbon nanotubes-based matrices designed for tissue engineering, focus on the biodegradability and long-term toxicity of CNTs. Chapter 10 in Materials for Biomedical Engineering: Bioactive Materials, Properties, and Applications. 1st edition. Grumezescu and Grumezescu (editors). Elsevier. 616 pages
Materials for Biomedical Engineering. 2020
 ">
">
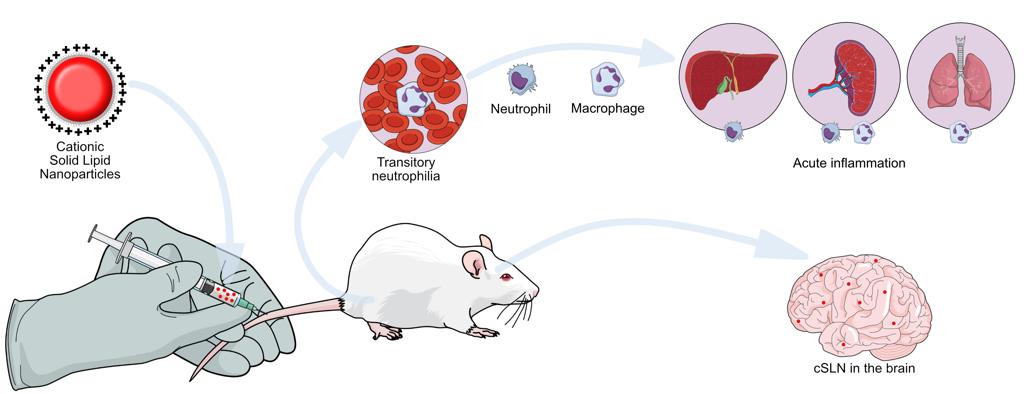
We found increases in the population of macrophages in the lungs, liver, and spleen and also migration of circulating neutrophils into inflamed tissue and a decrease in blood urea nitrogen. We also observed the presence of cSLNs within the brain parenchyma without any sign of damage to the blood-brain barrier. These side effects appeared to be mild and transitory (< 72 h). These findings reinforce the importance of investigating the toxicity of SLN-based formulations before the incorporation of drugs/genetic material to the formulation and its translation to the clinic.
Drug Delivery and Translational Research, Fev 2020
 ">
">
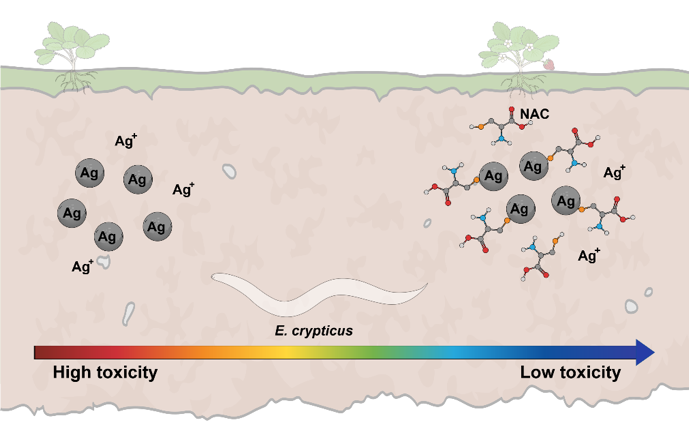
We hypothesized that the thiol-chelating compound N-acetylcysteine (NAC) could be used to reduce the toxic effects of AgNPs on soil invertebrates such as enchytraeids (Enchytraeus crypticus,Oligochaeta). This study presented novel evidence suggesting that N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) and glutathione (GSH) could be used to reduce the toxic effects of Ag materials on soil invertebrates such as enchytraeids (Oligochaeta, Enchytraeidae).
Environ Pollut. Jan 2020
 ">
">
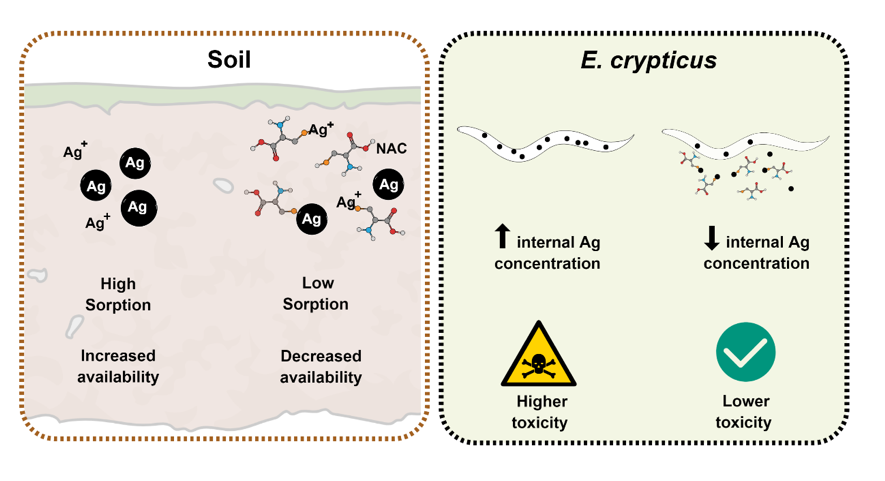
This study demonstrated that the toxicity of AgNPs to enchytraeid (Annelida: Oligochaeta) reproduction may be directly linked with high Ag availability in the soil therefore resulting in increased Ag bioaccumulation. NAC protects the Enchytraeus crypticus from toxicity of the AgNPs by reducing the concentration of Ag inside the organisms, rather than the rate at which Ag is entering the organism. Overall, we conclude that NAC could be an effective alternative for early remediation and recovery of terrestrial organisms exposed to metal-contaminated soils.
Sci Total Environ. Jan 2020